關於愛滋病
愛滋病(AIDS)的正式名稱是「後天免疫力缺乏症」,由愛滋病病毒(人類免疫力缺乏病毒, HIV)引起。
感染HIV後並不一定發病成為愛滋病患者。由於病毒會攻擊免疫系統,當感染者的免疫能力減弱,感染了一些對非感染者不會致病的病原體,便會發病成為愛滋病患者。
縱使HIV感染現時不能被根治,服用抗病毒藥物能夠抑制病毒複製。及早開始接受治療能夠維持預防發病及減少其他相關健康問題,壽命可與非感染者相若。藥物能夠將病毒數量減低至無法被偵測的水平,使免疫力能夠維持在正常水平;而且如果能夠維持無法被偵測的病毒數量半年或以上,患者將不會透過性接觸傳播HIV。
感染者的血液、精液、射精前液、直腸分泌物、陰道分泌物、母乳都有HIV病毒。若你的黏膜組織(包括陰莖頭、直腸、陰道、口腔)或新鮮傷口接觸到帶病毒的體液,便有機會受到感染。因此,HIV能夠透過性接觸、血液接觸和母嬰途徑傳染。相反,日常接觸如共同進食、接吻、擁抱和運動並不會傳播HIV。蚊叮蟲咬亦不會導致感染。
預防方法
- 避免共用針筒
- 正確使用安全套
- 事前預防用藥 (PrEP)
- 事後預防用藥 (PEP)
事前預防用藥 (PrEP)
PrEP是在有機會接觸到HIV前定期按時服藥以預防感染。但它不能取代安全性行為、亦沒有預防其他性病的能力。要有效預防愛滋病毒感染,須配合其他預防措施,包括使用安全套。此方法已獲世界衞生組織及美國藥物及食物管理局等監管機構認可。
事後預防用藥 (PEP)
PEP是一項緊急預防措施,在意外接觸到HIV後,如發生完高風險性行為,連續服藥28天以預防感染。PEP應在不遲於事後72小時內開始服藥,越早服藥效果越好。
診斷方法
最初感染HIV的二至四星期後,有些感染者會有類似感冒的病徵,例如發燒、疲倦、喉嚨痛、皮疹、腹瀉、胃口不佳、噁心和嘔吐。但並不是所有患者都有病徵,而且其他疾病亦可以引致這些病徵。因此,我們不能夠以病徵判斷是否感染HIV。接受愛滋病測試是確定有否感染的唯一方法。
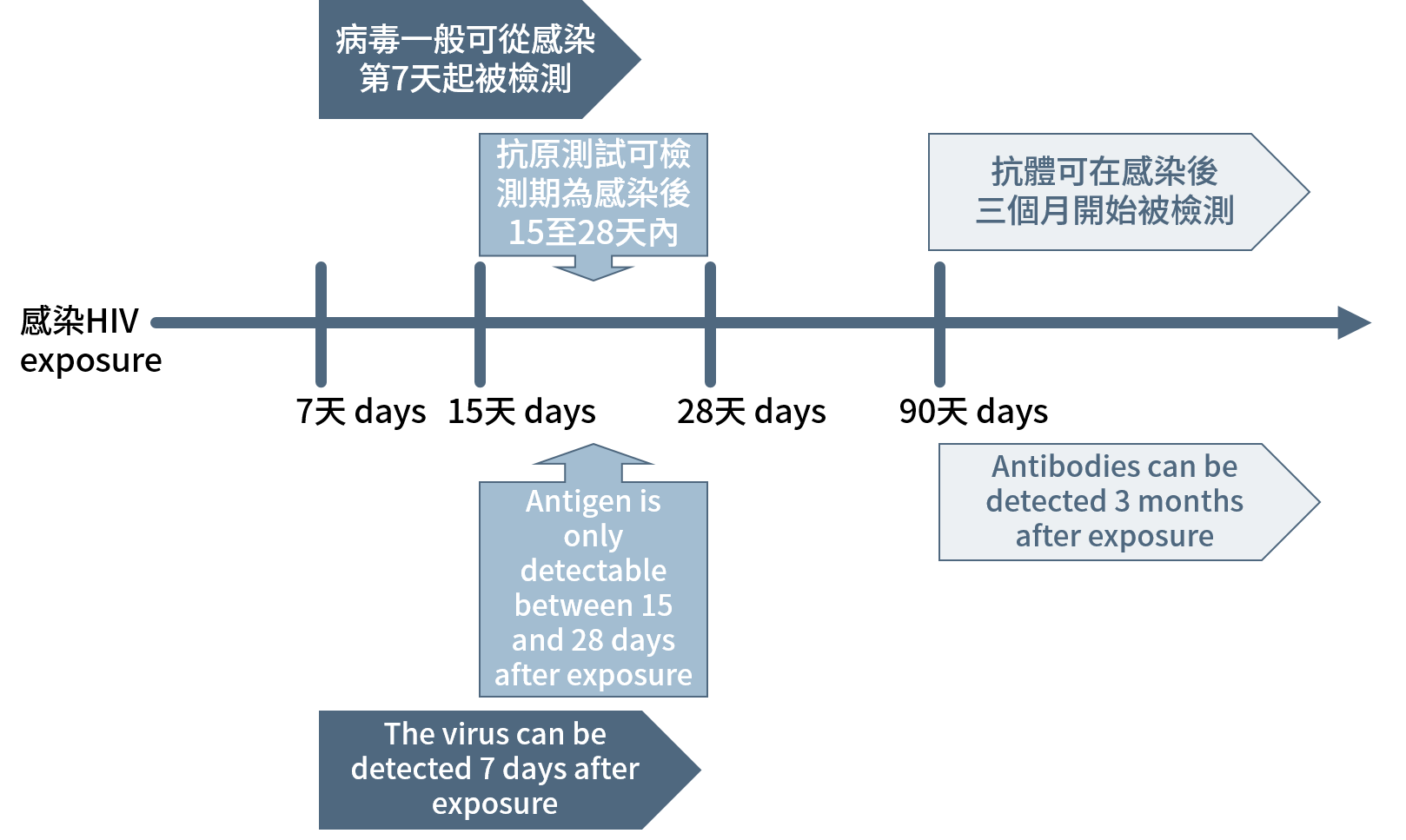
HIV抗體測試需要在空窗期後進行才能準確反映感染狀況。空窗期是由受到感染起計,直至身體產生足夠抗體至可被偵測水平,一般最長為三個月。在空窗期內檢測呈陰性並不代表沒有感染病毒,只是身體未產生足夠抗體。因此,你應該在發生令你擔心的行為的日期起計三個月後再做一次測試。快速測試能在短時間內提供結果作參考,但陽性結果需要由實驗室測試確認。服用事前或事後預防用藥(PrEP/PEP)或抗愛滋病病毒藥物可能會影響測試結果。因此一般不建議服用此等藥物的人士使用快速測試,而陰性結果不一定準確。
此研究計劃提供免費的自我檢測套裝。請按此閱讀更多關於自我檢測的資訊。
About HIV/AIDS
AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome) is a disease caused by a virus called HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus).
HIV infection has to be contrasted with AIDS. After infection, the virus will attack the immune system. When then immune system has been badly damaged that opportunistic infections occurred, the stage of HIV infection progressed to AIDS.
Although HIV infection can yet to be cured, taking antiretrovirals can suppress virus replication. Early initiation of treatment can prevent progression to AIDS and reduce risk of other related health problems that the life expectancy could be similar to HIV-uninfected people. Antiretroviral treatment could reduce the viral load to undetectable level, such that the immune system could be protected. Also, if the viral load could be maintained to be undetectable for at least half a year, the risk of sexual transmission is minimal.
HIV could be found in blood, semen, precum, rectal and vaginal secretions, and breast milk in people living with HIV. When your mucosal tissue (such as glans, rectum, vagina and mouth) or an open wound contacts with fluid with virus, there is an infection risk. On the contrary, daily activities such as eating, kissing, hugging, exercising do not carry risk of HIV infection, nor do insect bites.
Prevention
- Avoid syringe sharing
- Use condom correctly
- Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP)
- Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP)
Pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP)
PrEP is a means of HIV infection by taking medicines regularly before potential contract with HIV. It cannot replace condom, nor can it prevent other sexually transmitted infections. To effectively prevent HIV infection, one must also take other prevention measures such as using condom. PrEP has been approved by, among other regulatory authorities, World Health Organization and US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP)
PEP is an emergency measure taken after accidental contract with HIV, such as condomless sex or needlestick injury. PEP is a 28-day treatment which should be started no later than 72 hours post-exposure. Its efficacy is the best when started early.
Diagnosis
During the first 2-4 weeks after contracting with HIV, some patients suffered from flu-like symptoms such as fever, fatigue, sore throat, rash, diarrhoea, loss of appetite, nausea, vomit. As not all patients would suffer these symptoms and other diseases can also be the cause, symptoms are not definitive for making a diagnosis for HIV infection. Receiving HIV test is the only way to diagnose HIV infection.
HIV antibody test has to be conducted after window period to accurately reflect the true infection status. Window period is the period between infection and the time when the antibody produced by the body reaches a detectable level, which could be as long as 3 months. A negative test result within the window period does not imply one free from HIV infection, but rather the antibody level is insufficient to be tested. Therefore, you should get tested 3 months after the event potentially makes you infected. Rapid test offers a quick result for your reference, but a positive test result requires confirmation in laboratory. Taking antiretrovirals, including PEP and PrEP, may affect the test result. Therefore in general it is not recommended for people on antiretroviral treatment to use rapid test as a negative result can be unreliable.
This research project offers free HIV self-tests. Click here for more information about HIV self-tests.
香港中文大學何鴻燊防治傳染病研究中心
Stanley Ho Centre for Emerging Infectious Diseases, The Chinese University of Hong Kong
電郵地址 Enquiry: hello [at] test4you.online

香港中文大學 – 新界東醫院聯網臨床研究倫理 聯席委員會被授權在有需要時審視個人資料藉以評估研究倫理。
如果你有更多關於臨床研究倫理相關問題,請與該委員會聯繫(電郵 crec [at] cuhk.edu.hk)。
The Joint Chinese University of Hong Kong – New Territories East Cluster (CUHK-NTEC) Clinical Research Ethics Committee is authorized to access the subjects' records related to the study for ethics review purpose.
For enquiry regarding clinical research ethics, please contact the committee at crec [at] cuhk.edu.hk.